Following this SEO checklist helped us grow our blog traffic to over 640,000 monthly search visits.
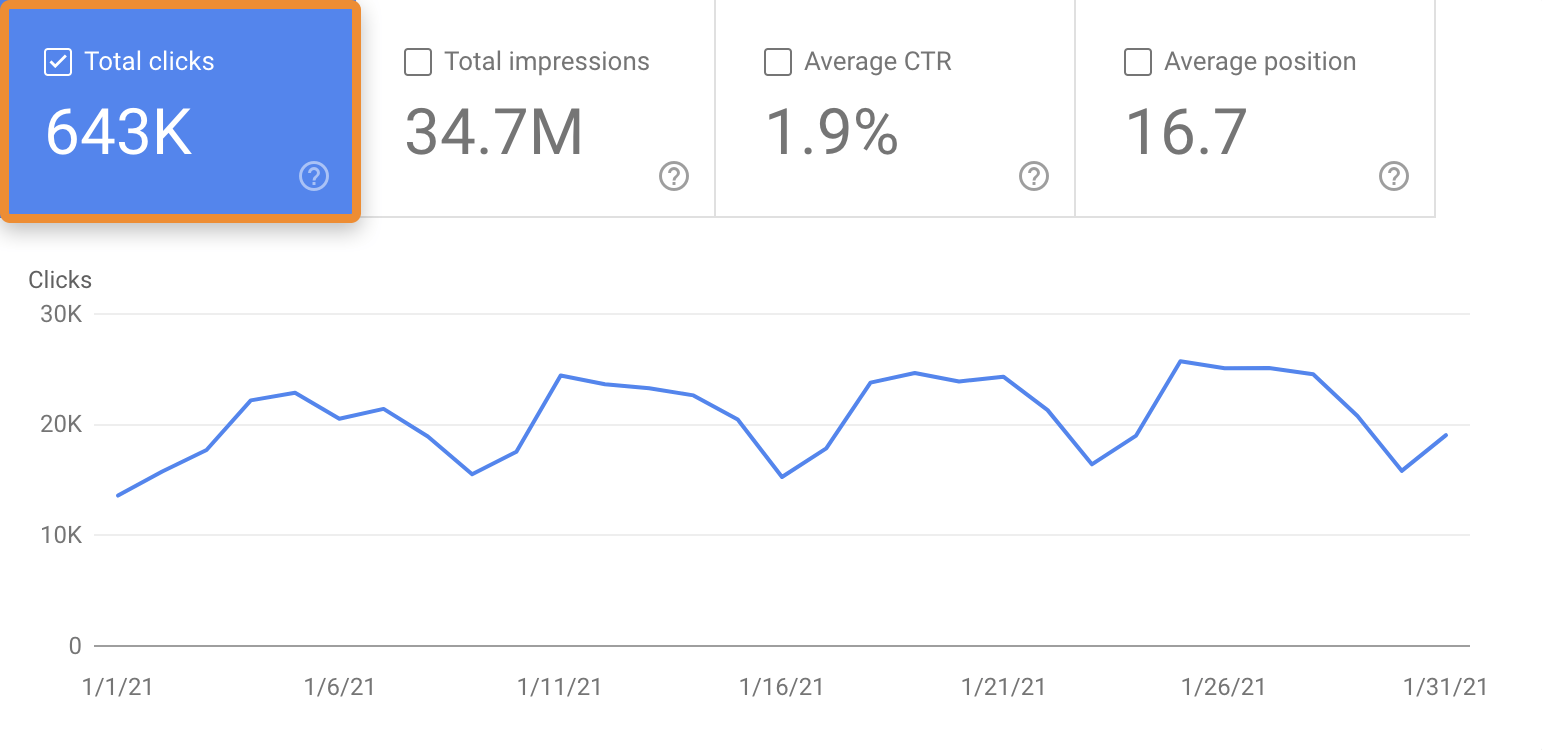
It works for ecommerce stores, local businesses, affiliate sites—anything.
Here’s the checklist:
- Basic SEO checklist
- Technical SEO checklist
- Keyword research checklist
- Content checklist
- On-page SEO checklist
- Link building checklist
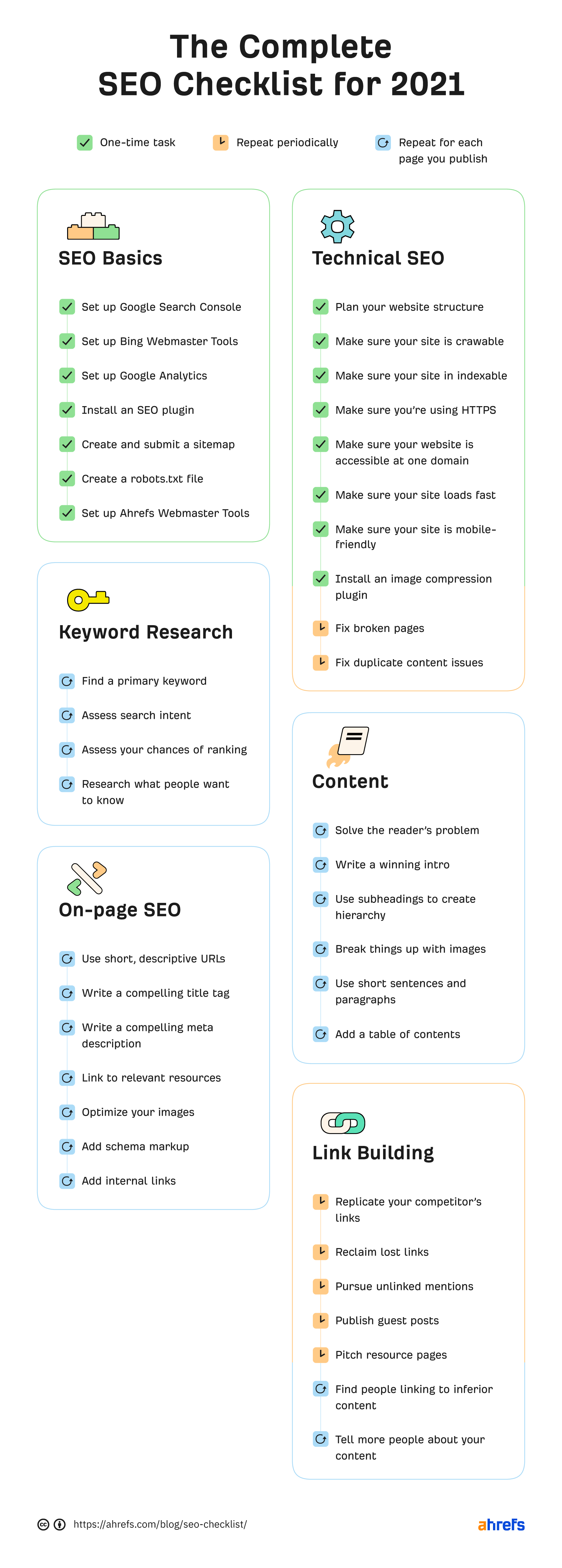
How to use this SEO checklist
Most SEO checklists fail to communicate how SEO is an ongoing process. Instead, they list random tasks and make it sound like SEO is done and dusted once you check them off.
That’s not the case, so we’ve given each item on our checklist one of these tags:
- Do it once
- Do it periodically
- Do it each time you publish a new page
This structure means you don’t need to go through everything on this checklist today. Do the one-time tasks first, then the periodic tasks, then complete the ongoing tasks each time you publish a new page.
Let’s get to it.
Let’s start with a few SEO best practices everyone should have in the bag. These won’t directly improve rankings, but they’re important in setting yourself up to rank higher in Google.
1. Set up Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a free tool for tracking your site’s organic search performance.
Here are a few things you can do with it:
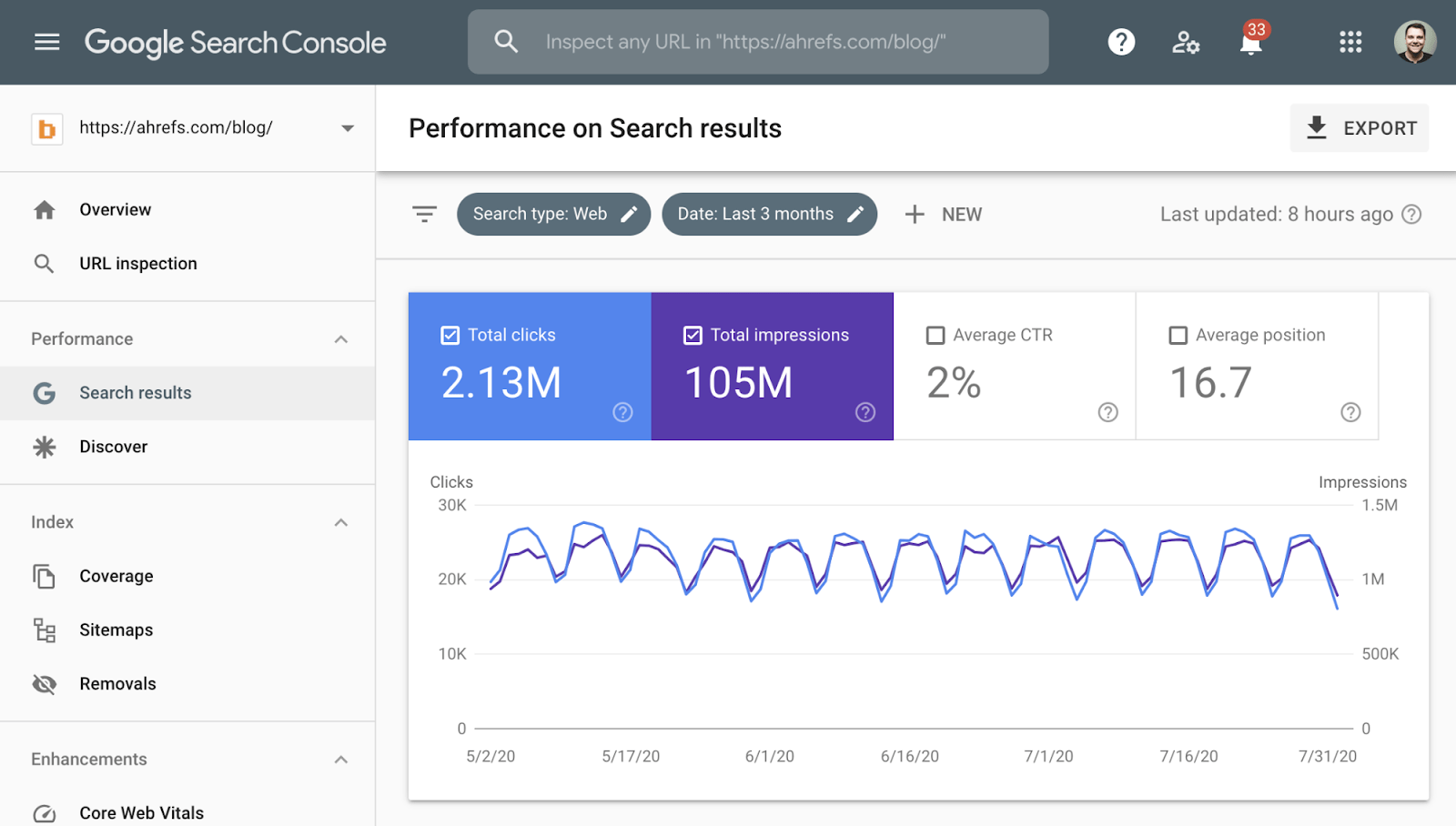
Learn how to set it up in our step-by-step guide.
2. Set up Bing Webmaster Tools
Bing Webmaster Tools is essentially Bing’s equivalent of Google Search Console.
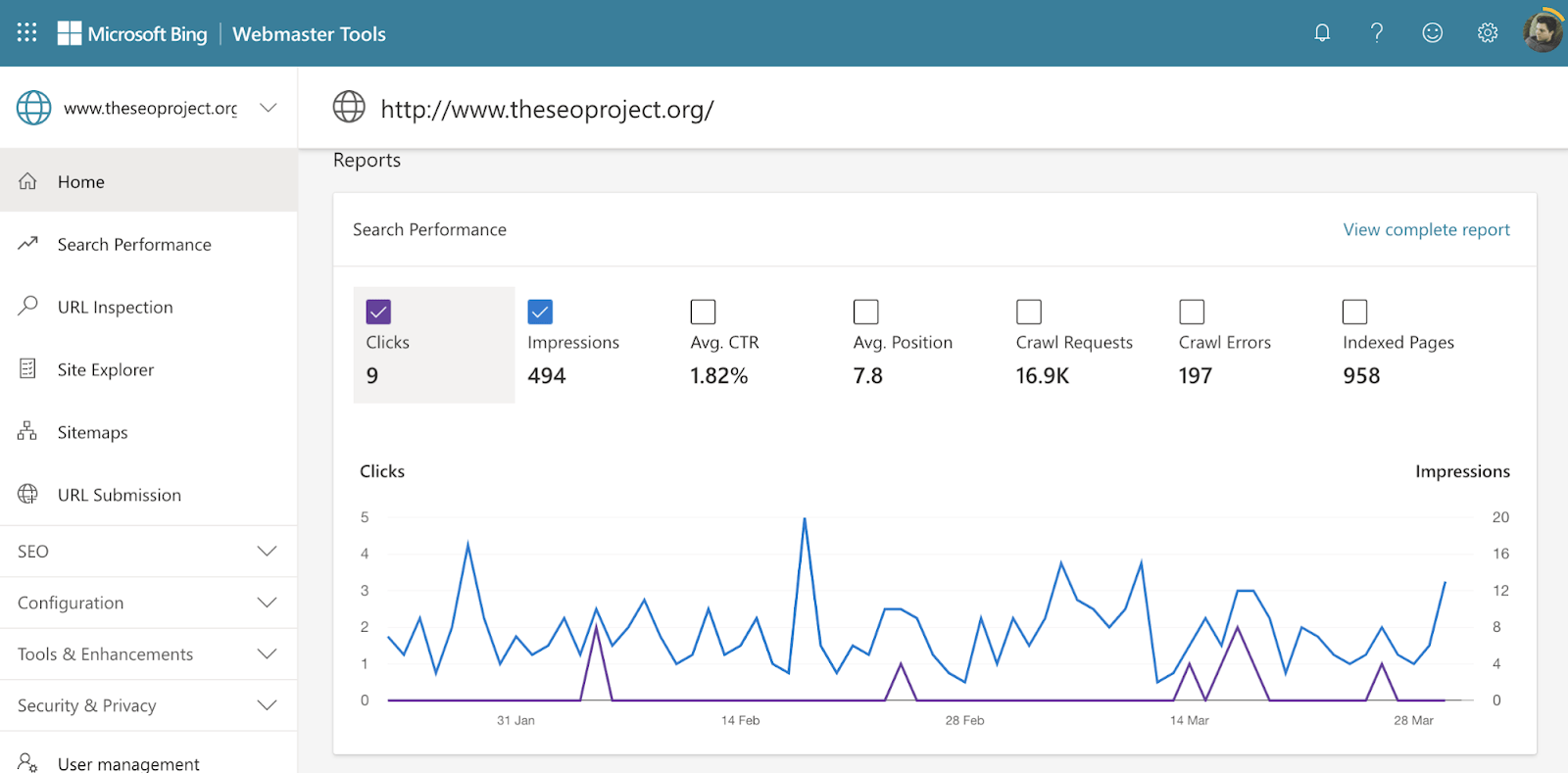
Learn how to set it up here.
3. Set up Ahrefs Webmaster Tools
Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT) is a free tool that helps you improve your website’s SEO performance and get more organic search traffic.
Here are a few key features:
- Scan your site for 100+ SEO issues
- See all your backlinks
- See all the keywords you rank for
Learn more about AWT here:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ipTk-qGrNlc
4. Set up Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a free tool that lets you see how many people are visiting your site, where they’re coming from, and how they’re interacting with it.
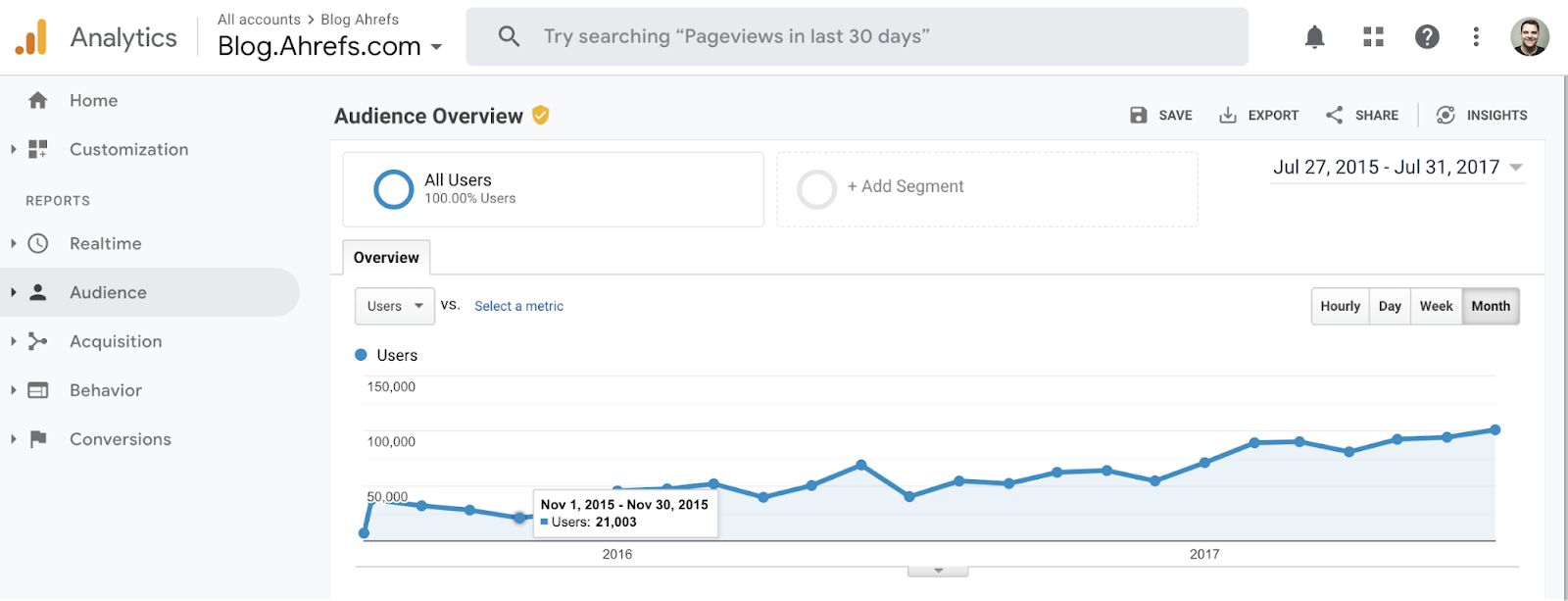
Learn how to set it up in this guide.
Sidenote.
It’s also worth linking Google Search Console with Google Analytics to see Search Console data in Analytics. Learn how to do that here.
Recommended reading: How to Use Google Analytics to Improve SEO Performance
5. Install an SEO plugin
If you’re using WordPress, you’ll need an SEO plugin to help you optimize things like sitemaps and meta tags.
Here are a few good options (you only need one):
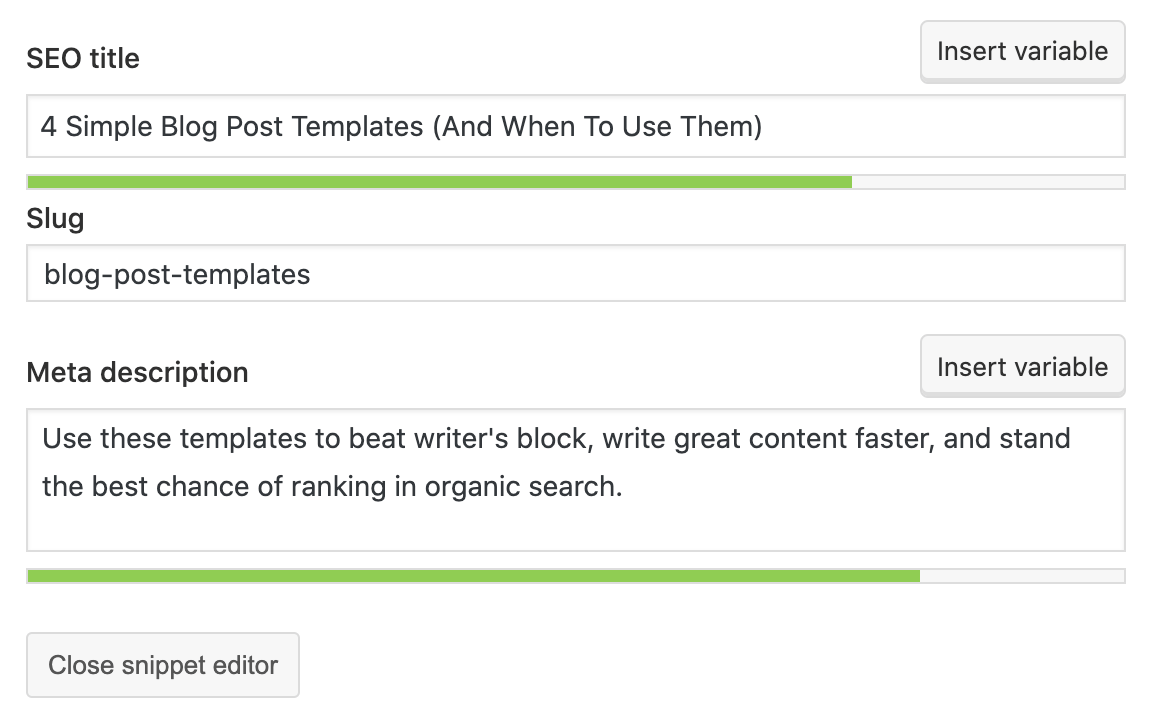
Adding a meta title and description with Yoast.
If you’re using a different website platform like Shopify, you probably don’t need an SEO plugin.
6. Create and submit a sitemap
Sitemaps tell search engines where to find important content on your site so they can easily crawl and index your pages.
Here’s what the sitemap looks like for our blog:
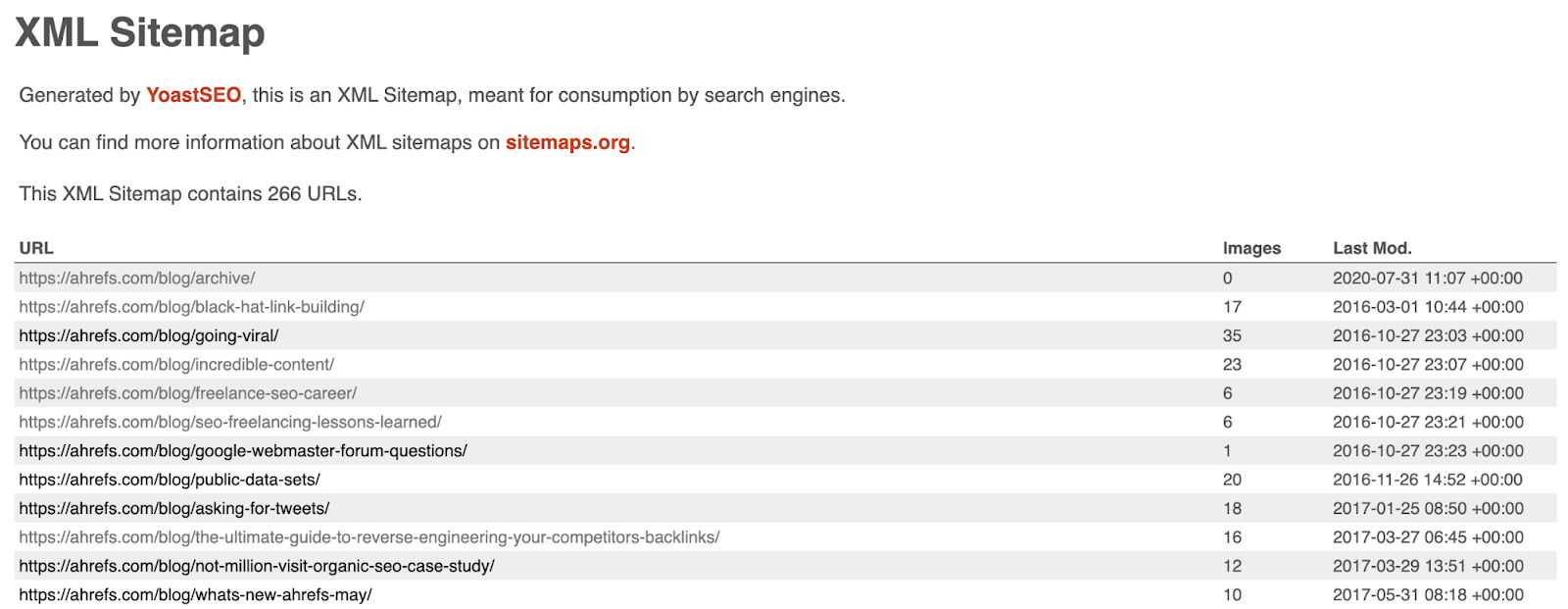
You can usually find your sitemap at one of these URLs:
/sitemap.xml/sitemap_index.xml/sitemap
Read this if you can’t find it, then learn how to submit your sitemap to Google and Bing here.
7. Create a robots.txt file
Robots.txt is a plain text file that tells search engines where they can and can’t go on your site.
It’s always good practice to have a robots.txt file, but it’s a must if you need to prevent search engines from crawling pages or sections on your site. For example, if you run an ecommerce store, you might not want them to crawl and index your cart page.

You can check if you already have a robots.txt file by going to yourdomain.com/robots.txt. If you see a plain text file, you’re good to go. If you see anything else, search Google for “robots.txt generator” and create one.
Recommended reading: Robots.txt and SEO: Everything You Need to Know
Technical SEO issues often hold a website back from ranking as high as it deserves. Here are the basic technical best practices everyone should follow.
8. Plan your website structure (new sites only)
It’s crucial that visitors and search engines can easily navigate your website. That’s why you need to create a logical site structure.
To do this, sketch out a simple mind map:
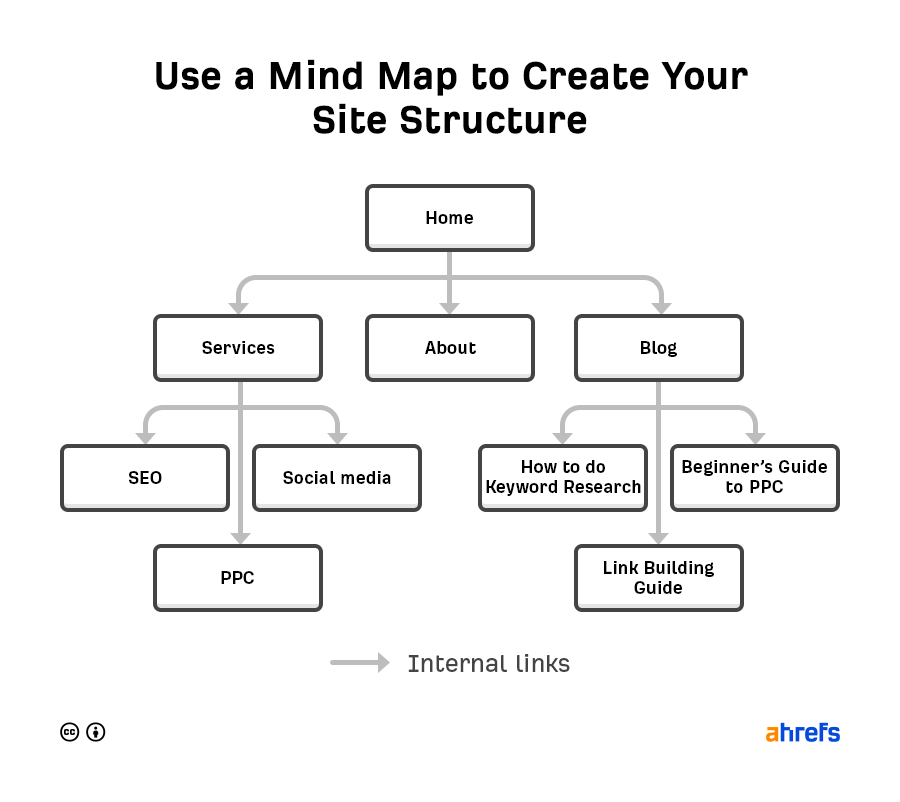
Each branch on the map should be an internal link to allow search engines and visitors to navigate between pages.
Recommended reading: Website Structure: How to Build Your SEO Foundation
9. Make sure your site is crawlable
Google can’t properly index content that isn’t crawlable, so it’s worth checking the Coverage report in Google Search Console for any warnings or exclusions relating to robots.txt.
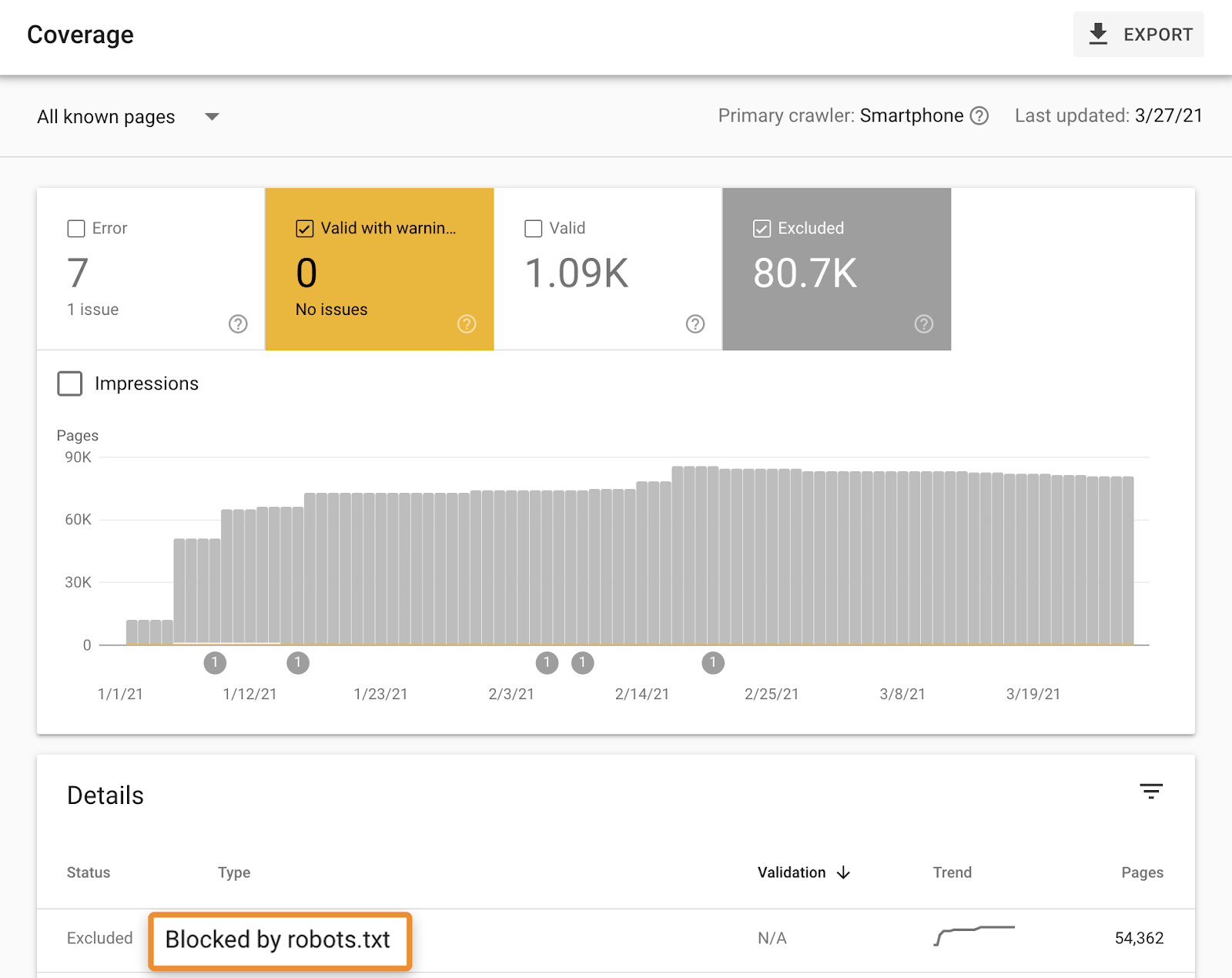
If you want Google to make sure Google indexes any of the blocked pages correctly, you should remove the rule that’s causing the block from your robots.txt file.
Recommended reading: Robots.txt and SEO: Everything You Need to Know
10. Make sure your site is indexable
Indexing and crawling are two different things. Just because search engines can crawl a page doesn’t mean they can index it. If there’s a ‘noindex’ robots meta tag or x‑robots-tag on the page, indexing isn’t possible.
Google tells you about noindexed URLs in the Coverage report.
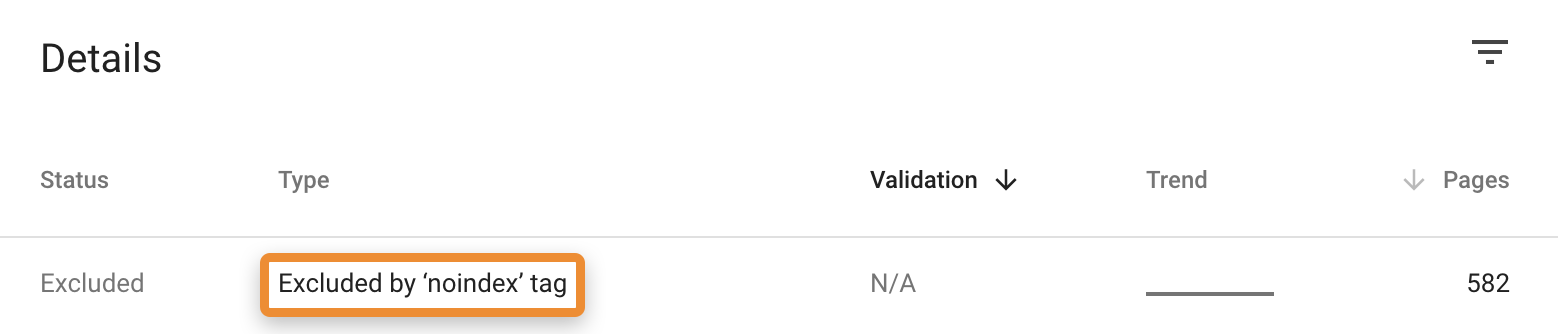
You can also find this information in the Indexability report in Ahrefs’ Site Audit.
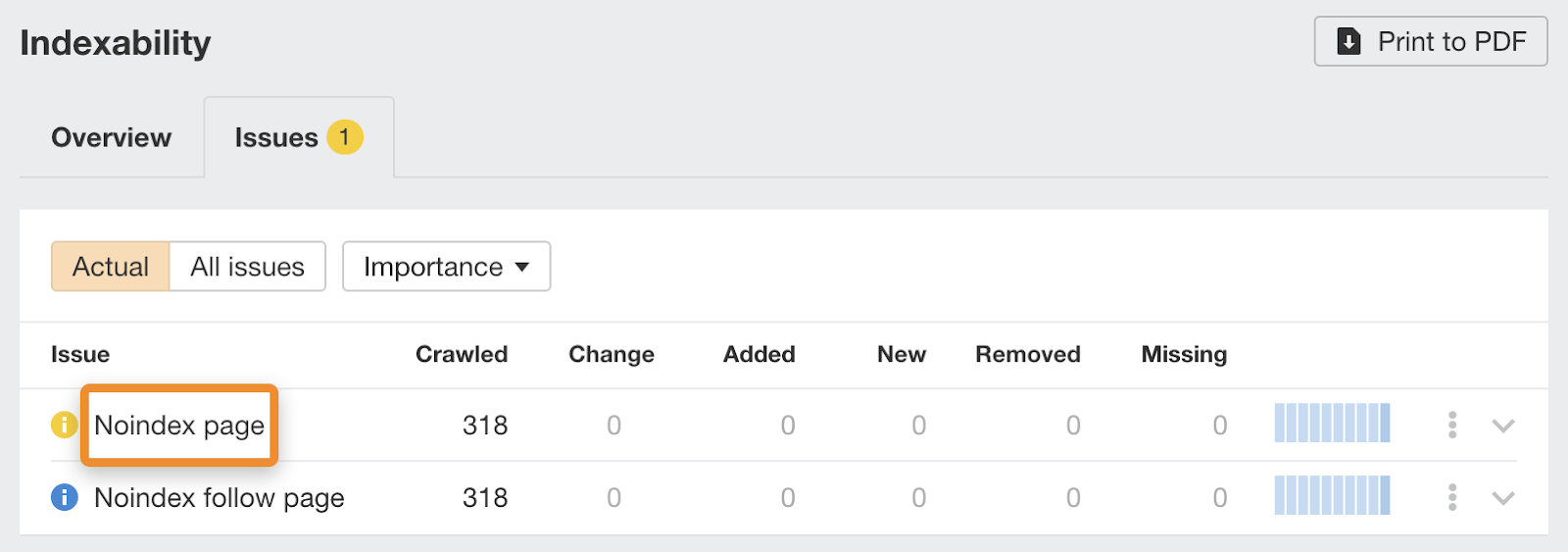
If you have ‘noindexed’ pages that should be indexed, remove the ‘noindex’ tag.
Recommended reading: Robots Meta Tag & X‑Robots-Tag: Everything You Need to Know
11. Make sure you’re using HTTPs
HTTPS is a confirmed lightweight ranking factor.
Yeah, that’s wrong. HTTPS is not a factor in deciding whether or not to index a page, at all. We do use HTTPS as a light-weight ranking factor, and having HTTPS is great for users. A free certificate from Let’s Encrypt works just as well.
— 🍌 John 🍌 (@JohnMu) January 29, 2019
If you’re not using HTTPS today, it’s time to make the switch.
Potential ranking boosts aside, HTTPS will protect your visitors’ data. This is especially important if you have any contact forms on your site. If you’re asking for passwords or payment information, then it’s not just important; it’s an absolute must.
How do you know if your site uses HTTPS?
Look for a padlock in your browser’s search bar:

Sidenote.
You can get a free SSL certification from Lets Encrypt.
12. Make sure your website is accessible at one domain
Visitors shouldn’t be able to access your website at multiple locations. It can lead to crawling, indexing, and security issues.
To check that everything’s in order, plug these four URLs into httpstatus.io:
- http://yourdomain.com
- http://www.yourdomain.com
- https://yourdomain.com
- https://www.yourdomain.com
If everything’s good, three of them should redirect to the fourth.
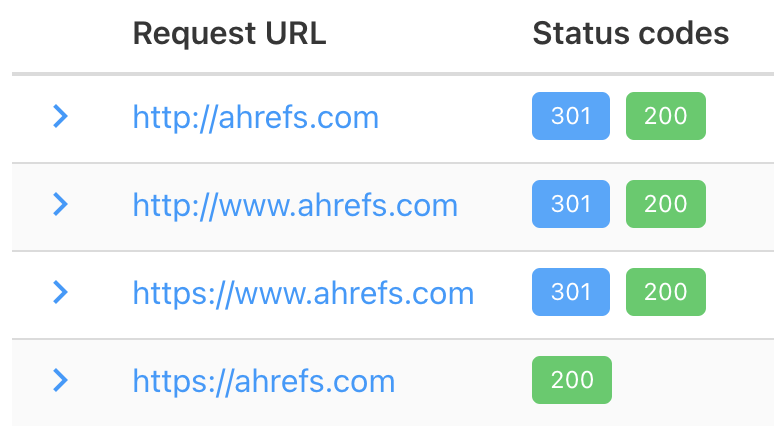
If that doesn’t happen, you need to set up a permanent 301 redirect.
If you’re using HTTPS (you should be), it’s also important that the accessible version of your website is the secure version. That’s either https://yourdomain.com or https://www.yourdomain.com.
Recommended reading: 301 Redirects for SEO: Everything You Need to Know
13. Make sure your site loads fast
Page speed has been a ranking factor on desktop since 2010 and mobile since 2018.
It’s easy to see why. It’s frustrating to click on a search result and have to wait for it to load. That’s why the probability of a bounce increases as page speed decreases.
You can use tools like PageSpeed Insights and GTMetrix to see how fast your web page loads.
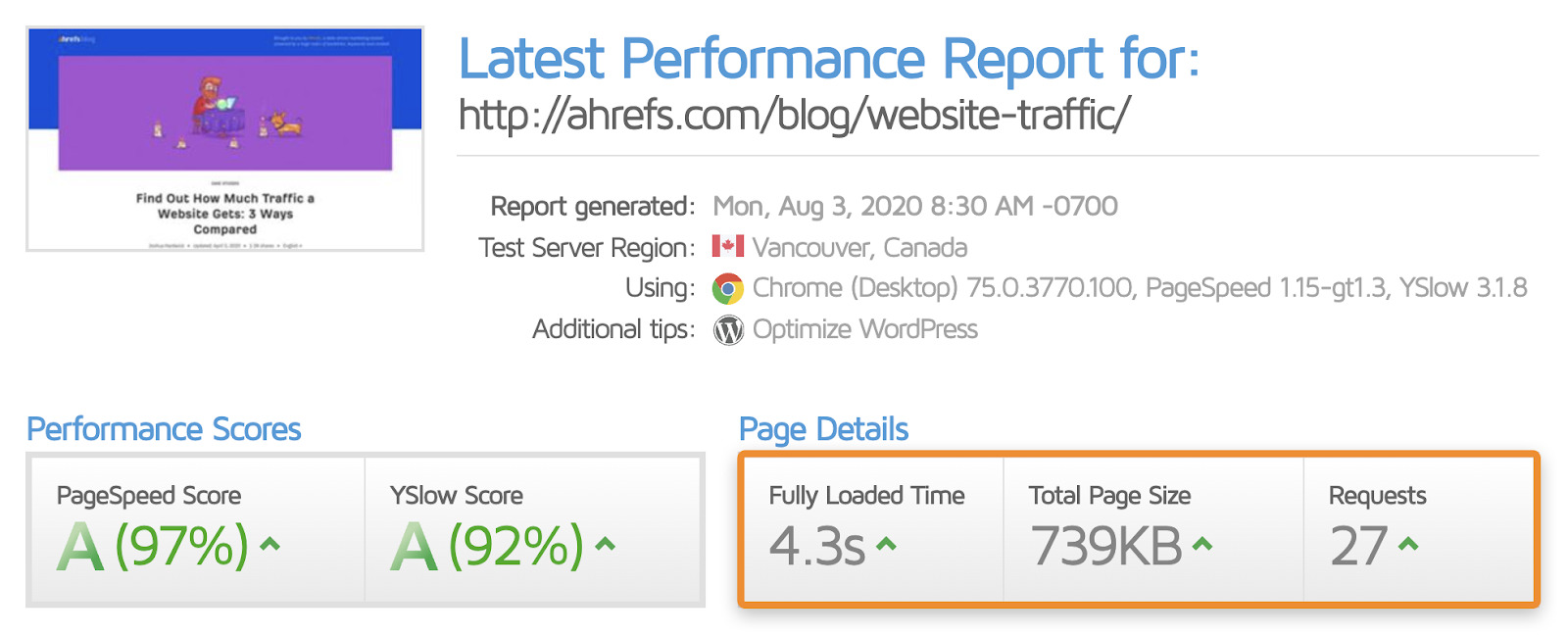
However, these tools can only check one page at a time. To check all your pages, crawl your site with Ahrefs’ Site Audit. You’ll see slow pages flagged in the Performance report.
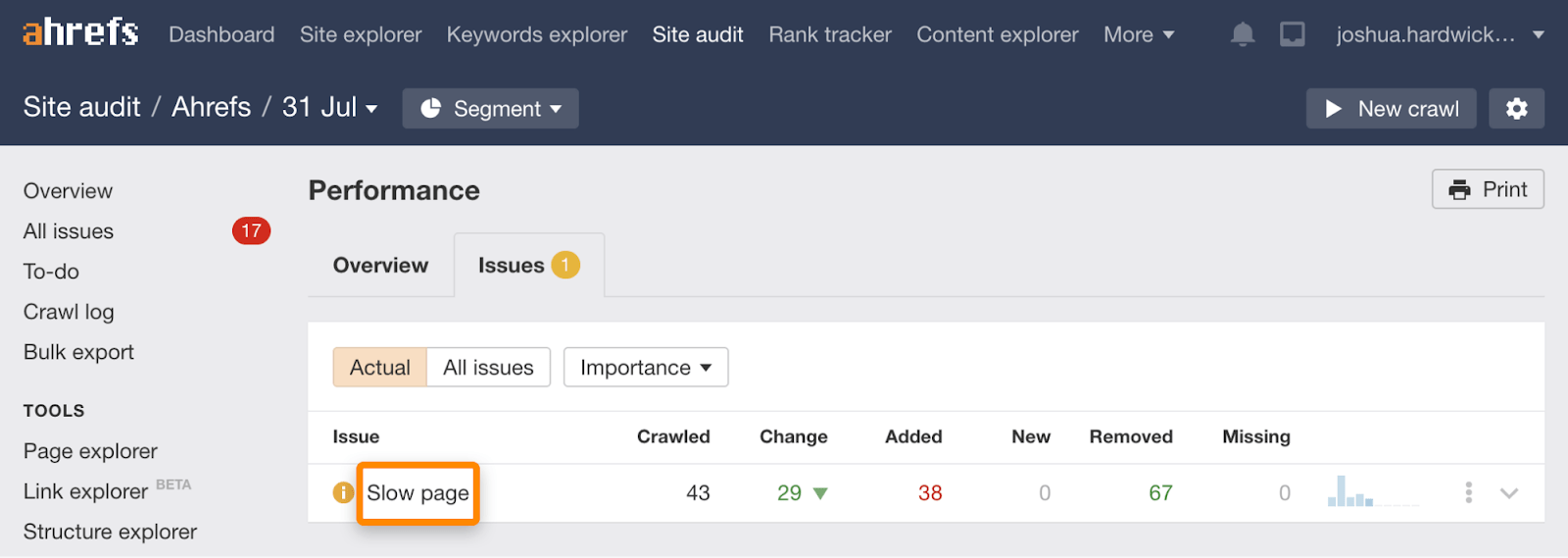
14. Make sure your site is mobile-friendly
Most searches happen on mobile devices, so having a mobile-friendly website is more important than ever.
Check whether your site needs work with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
15. Install an image compression plugin
Compressing images makes image files smaller and improves page speed. That’s important because page speed is a Google ranking factor.
If you’re using WordPress, there are plenty of plugins for this. We like ShortPixel. It lets you compress up to 100 images per month for free.
If you’re using another website platform, search Google for a suitable plugin or use ShortPixel’s web app.
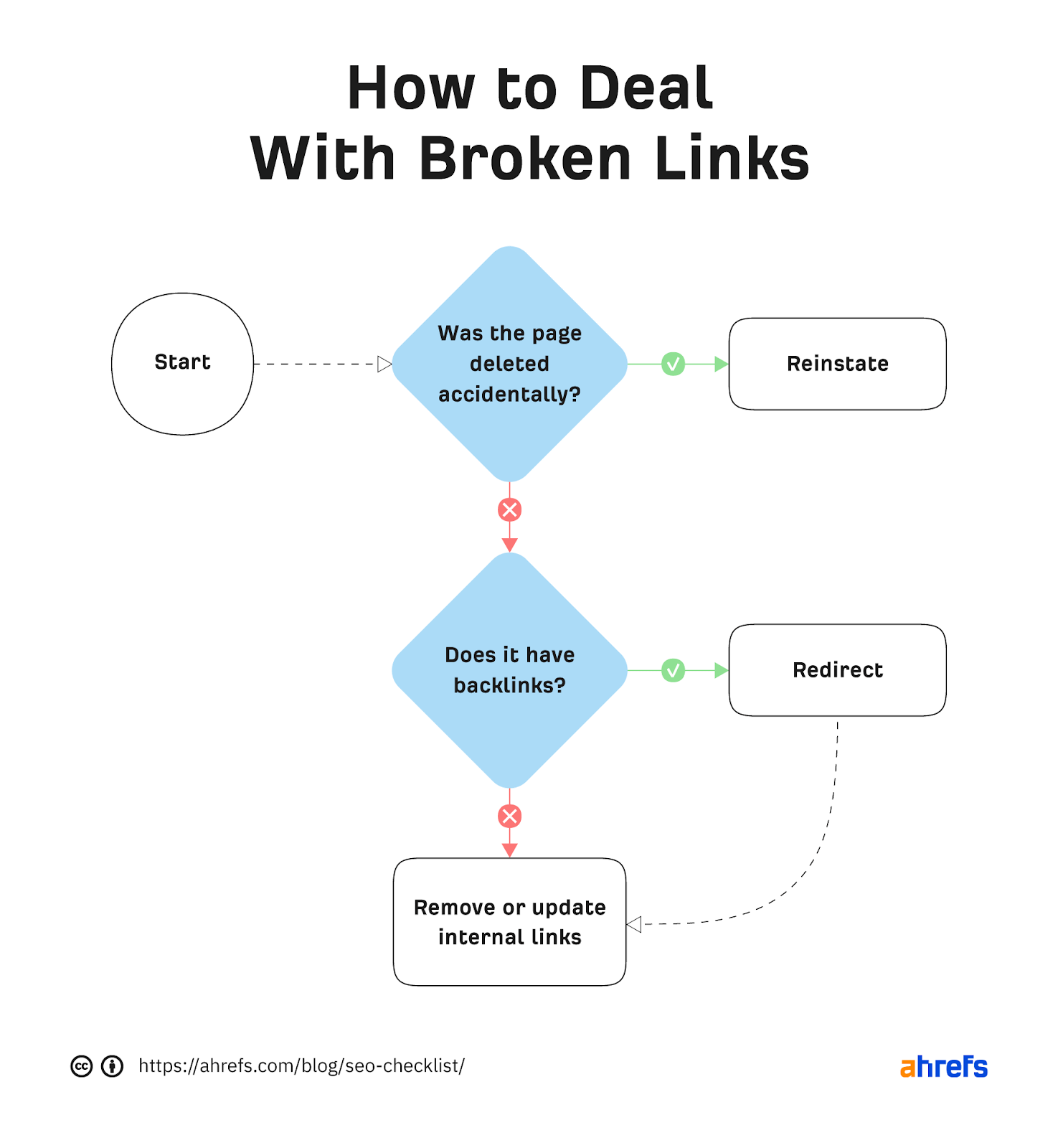
16. Fix broken pages
Broken links can negatively impact user experience and break the flow of ‘authority’ into and around your website.
To find broken links on your site, use Ahrefs Webmaster Tools.
- Crawl your website with Site Audit
- Go to the Internal pages report
- Look for “404 page” errors
Here’s how to deal with any broken links you find:
Recommended reading: How to Find and Fix Broken Links (to Reclaim Valuable “Link Juice”)
17. Fix duplicate content issues
Duplicate content is exact or near-duplicate content that appears on the web in more than one place. It’s a common ecommerce SEO issue thanks to faceted navigation. That alone can cause hundreds of duplicate content issues.
You can find duplicate content issues for free with Ahrefs Webmaster Tools.
- Crawl your website with Site Audit
- Go to the Duplicate content report
- Hit the “Issues” tab
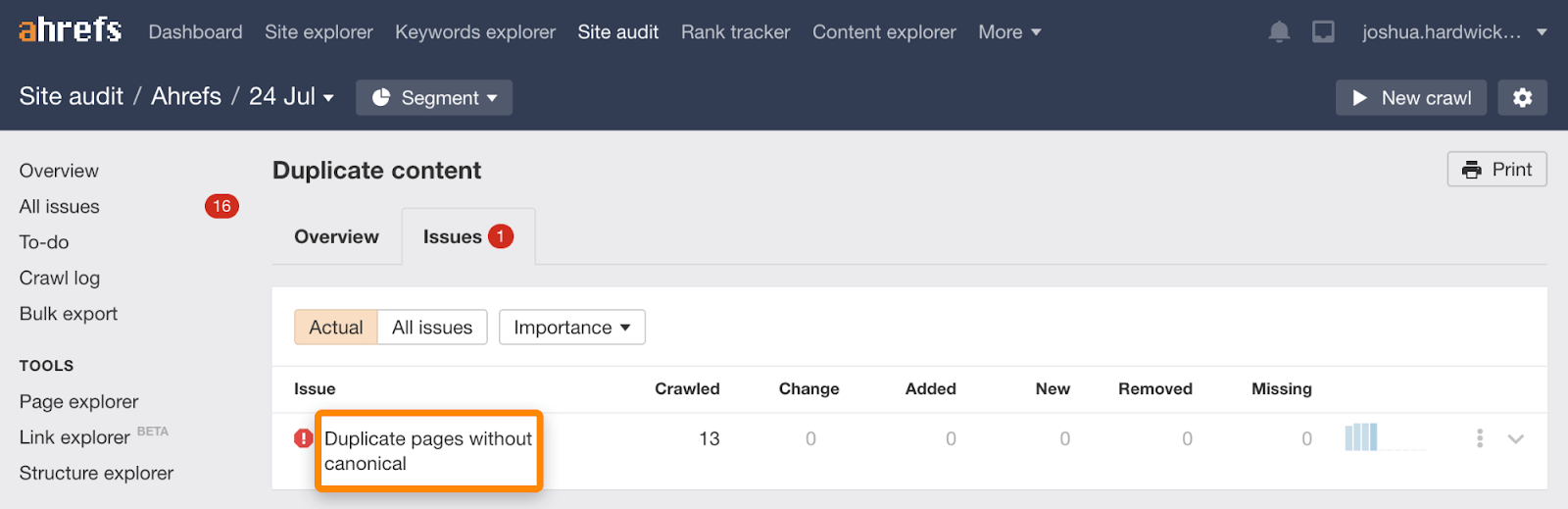
Fix these by canonicalizing the affected URLs where necessary.
Recommended reading: Duplicate Content: The Complete Guide for Beginners
Keyword research is the most crucial piece of the SEO puzzle. If you don’t know what keywords people are searching for, how can you possibly optimize your content for search engines?
Follow these checklist items to get off on the right foot.
18. Find a primary keyword to target
Each page on your website should target one main primary keyword. You should do keyword research periodically to find keywords to target, but you should also make sure you’re targeting the best keyword each time you publish a new page.
How do you know which is the best keyword?
It’s the one that represents the most popular way of searching for the topic.
For example, let’s say you were writing a post about the best protein powders. There are lots of ways people could search for this, such as:
- what is the best protein powder
- best protein supplements
- best protein shakes
So which one of these keywords do you target, if any?
Luckily, there’s an easy way to figure this out. Just search for your topic in Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer and look at the Parent Topic. This is usually a more popular way of searching for the same thing.
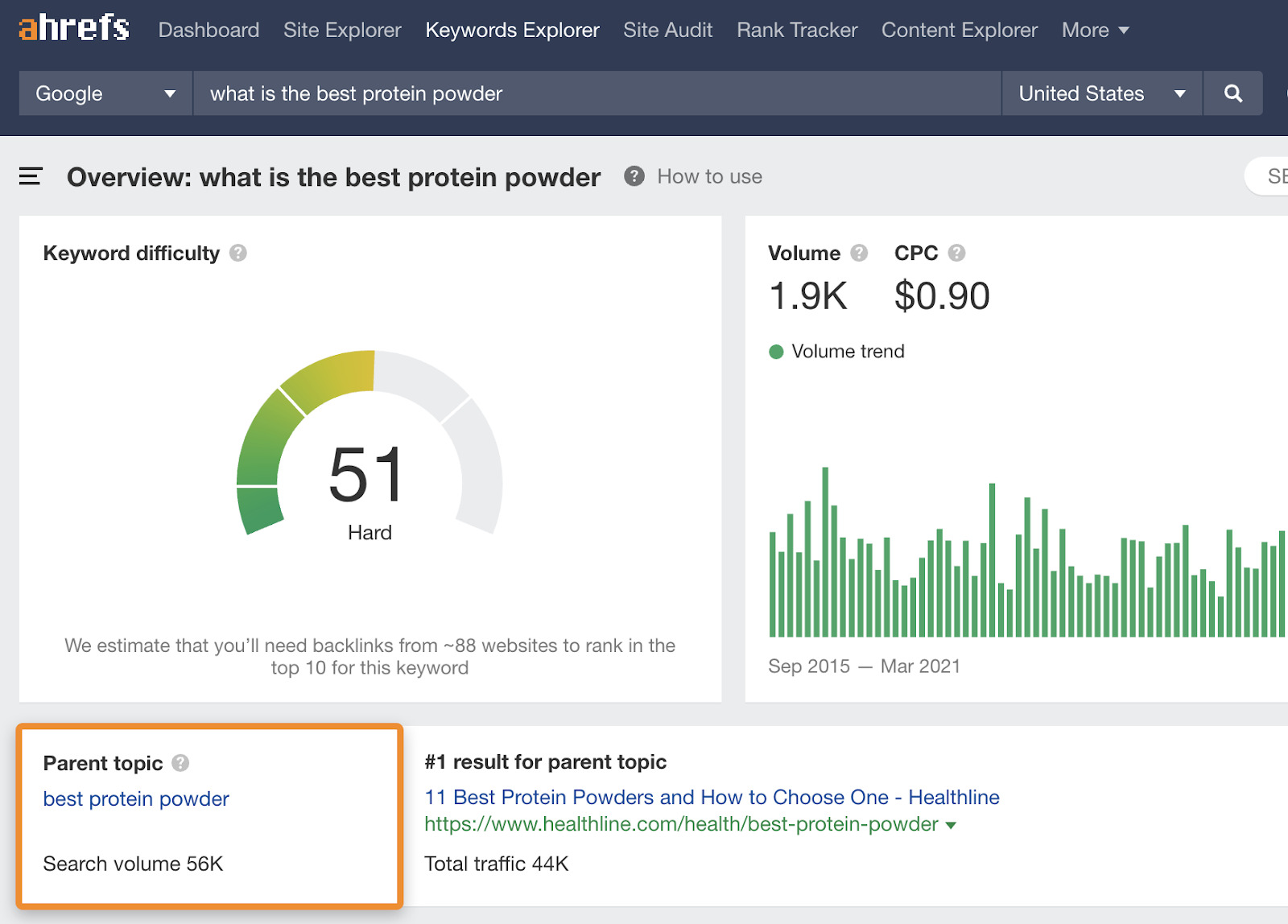
Sidenote.
Parent Topic isn’t 100% foolproof. It simply shows the keyword sending the most traffic to the top-ranking page for your keyword. This is usually the best keyword to target but not always, so don’t let this trump common sense.
Recommended reading: How To Do Keyword Research for SEO
19. Assess search intent
Search intent is the reason behind a searcher’s query. If your page doesn’t align with this, your chances of ranking are slim to none.
How do you assess search intent?
Look at the types and format of pages ranking in Google for your primary keyword.
For example, we can see from the URLs and titles of the top-ranking results for “marketing skills” that they’re all blog posts. As for the format, they’re mostly listicles.
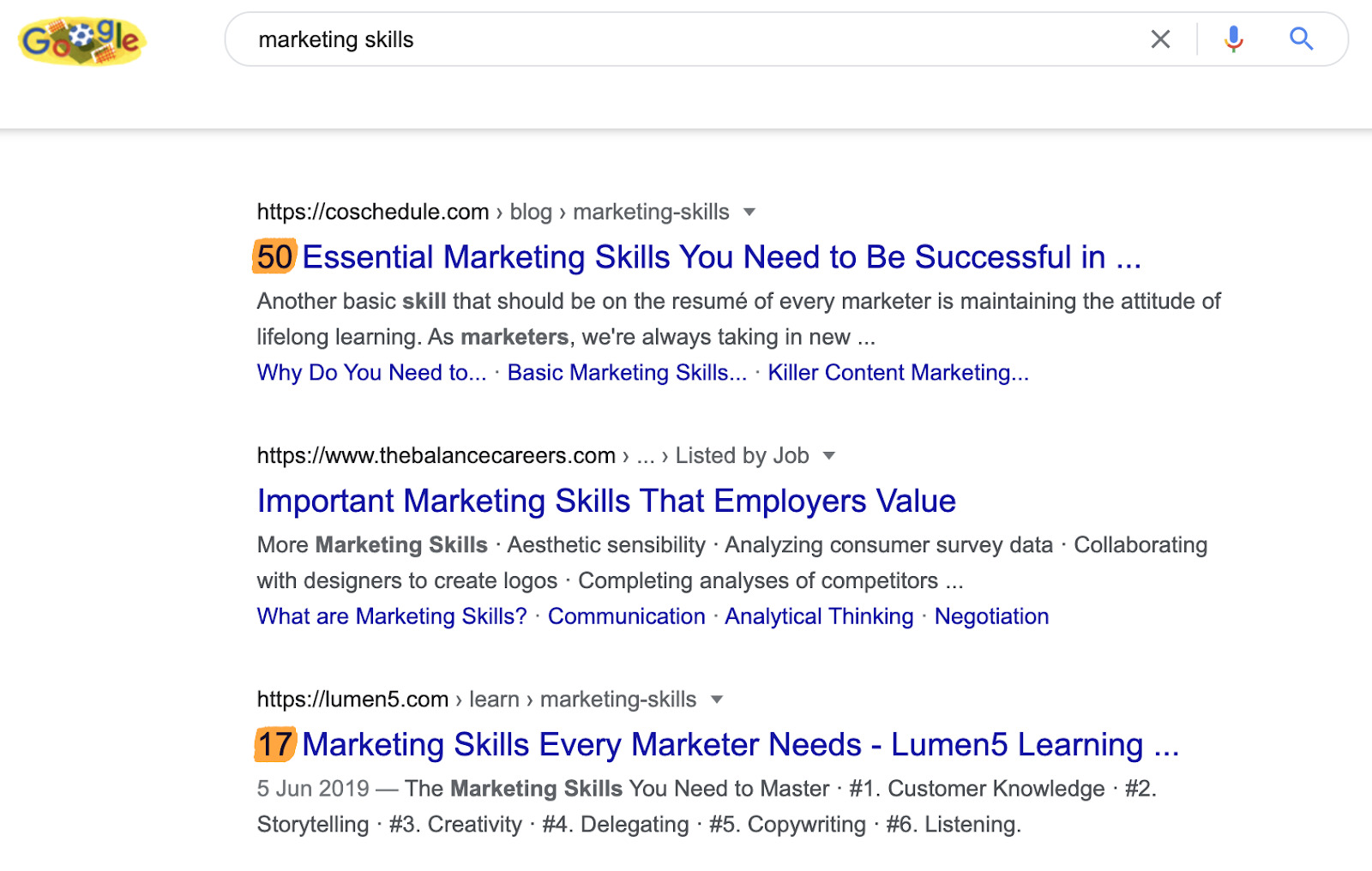
If you targeted this keyword with a page selling a course, you probably wouldn’t rank because it doesn’t match search intent.
Recommended reading: What is Search Intent? A Complete Guide for Beginners
20. Assess your chances of ranking in Google
Understanding the ease or difficulty of ranking for a keyword helps you to prioritize the opportunity and set realistic expectations.
For an initial rough estimate, use the Keyword Difficulty score in Keywords Explorer.
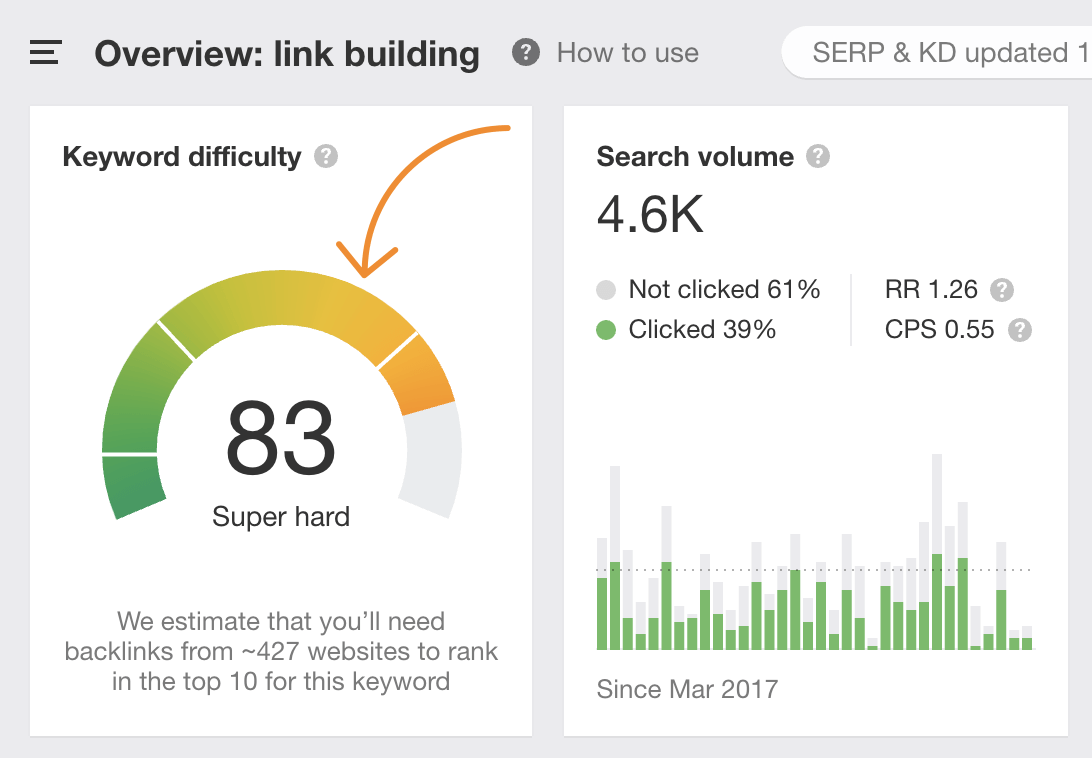
Just don’t rely on this entirely. Check the results yourself for things that may indicate a hard keyword to crack, like:
- High-quality backlinks to the top-ranking pages
- Predominantly big brands in the top 10
- High topical relevance of the top-ranking sites
Learn more in this tutorial.
21. Research what people want to know
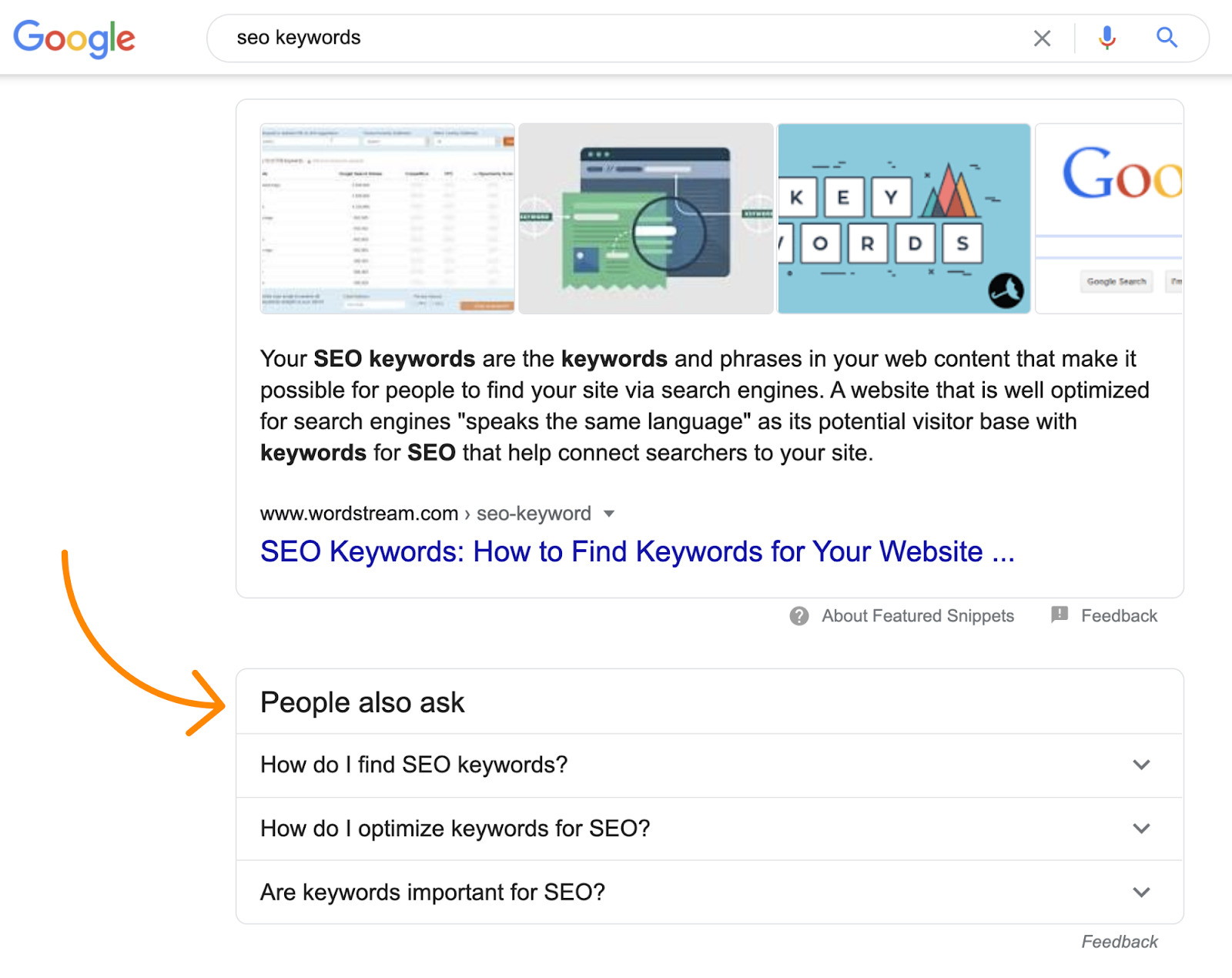
Say that someone searches for “SEO keywords.” You can see from analyzing search intent that people are looking for a definition of the term, but what other questions do they have? And what other information should you include in your content?
Google’s “People Also Ask” box gives some insight into this:
For more ideas, take three top-ranking pages and paste them into Ahrefs’ Content Gap tool. This will show you the keywords that one or more of the pages rank for.
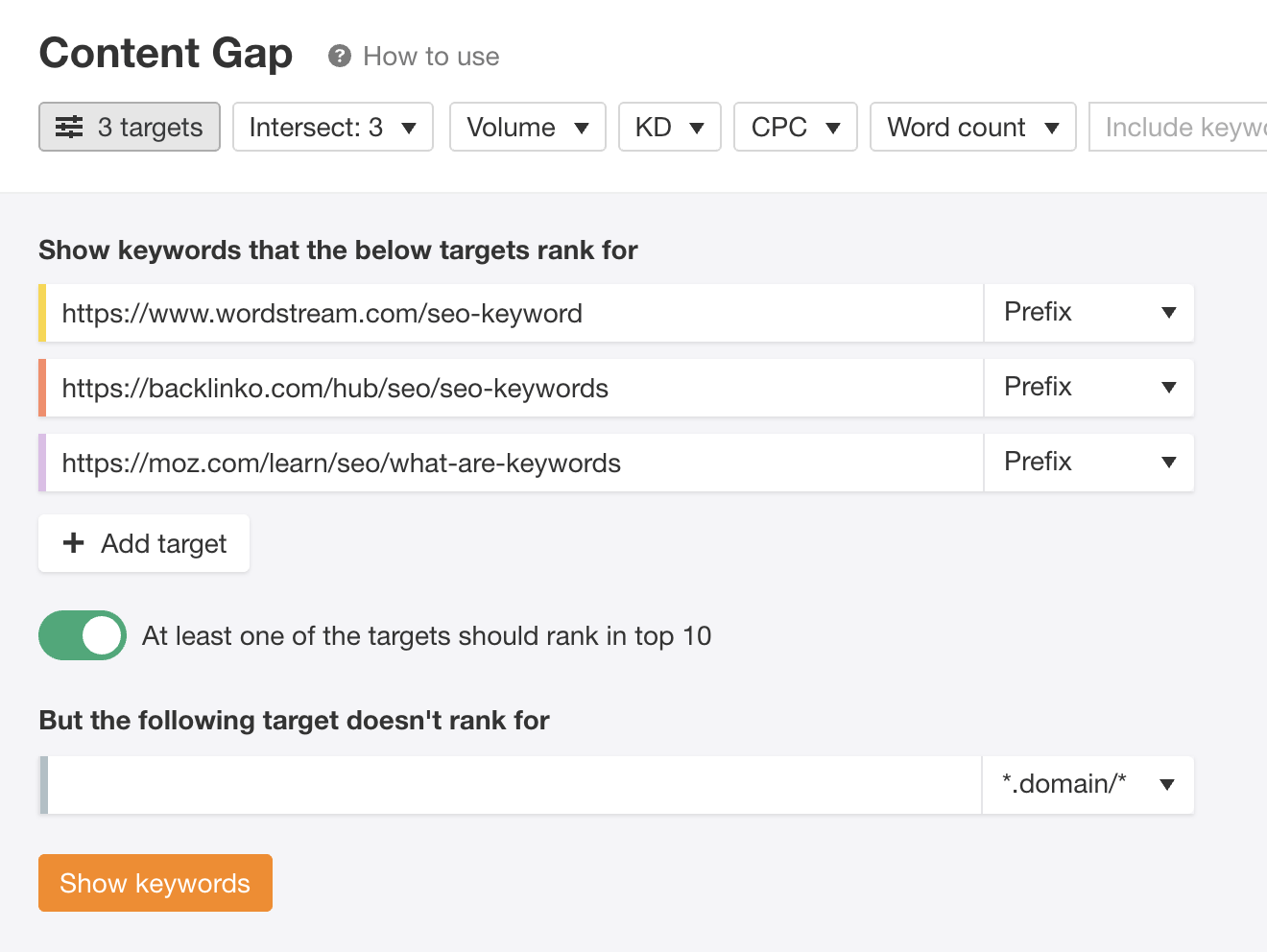
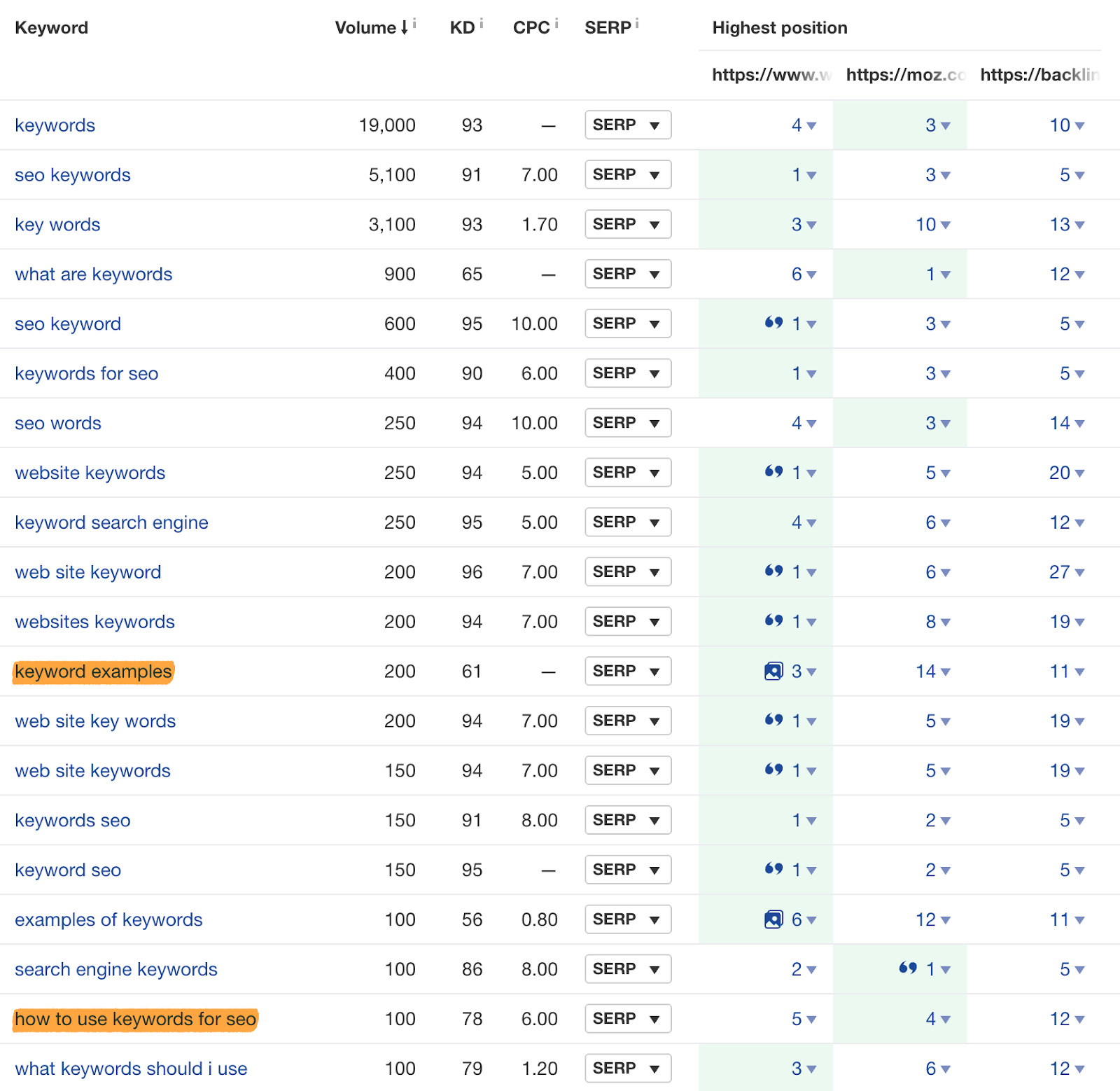
It’s then just a case of eyeballing the results for keywords that might represent subtopics. In our case, that might be “keyword examples” and “how to use keywords for SEO.”
Picking the right keyword is important, but all your efforts will be in vain if your content isn’t up to scratch. Follow these tips to level up your content.
22. Solve the reader’s problem
Understanding search intent is the first step of solving the reader’s problem because it tells you what kind of content they’re looking for.
Research is another important step.
But to create truly great content, you need to go further and really consider the visitor’s problem.
For example, take a query like “productivity tips.” It’s clear from assessing search intent that searchers want a listicle-style blog post. And if we research the top-ranking posts, we see common advice like “take breaks” and “put things down on paper.”
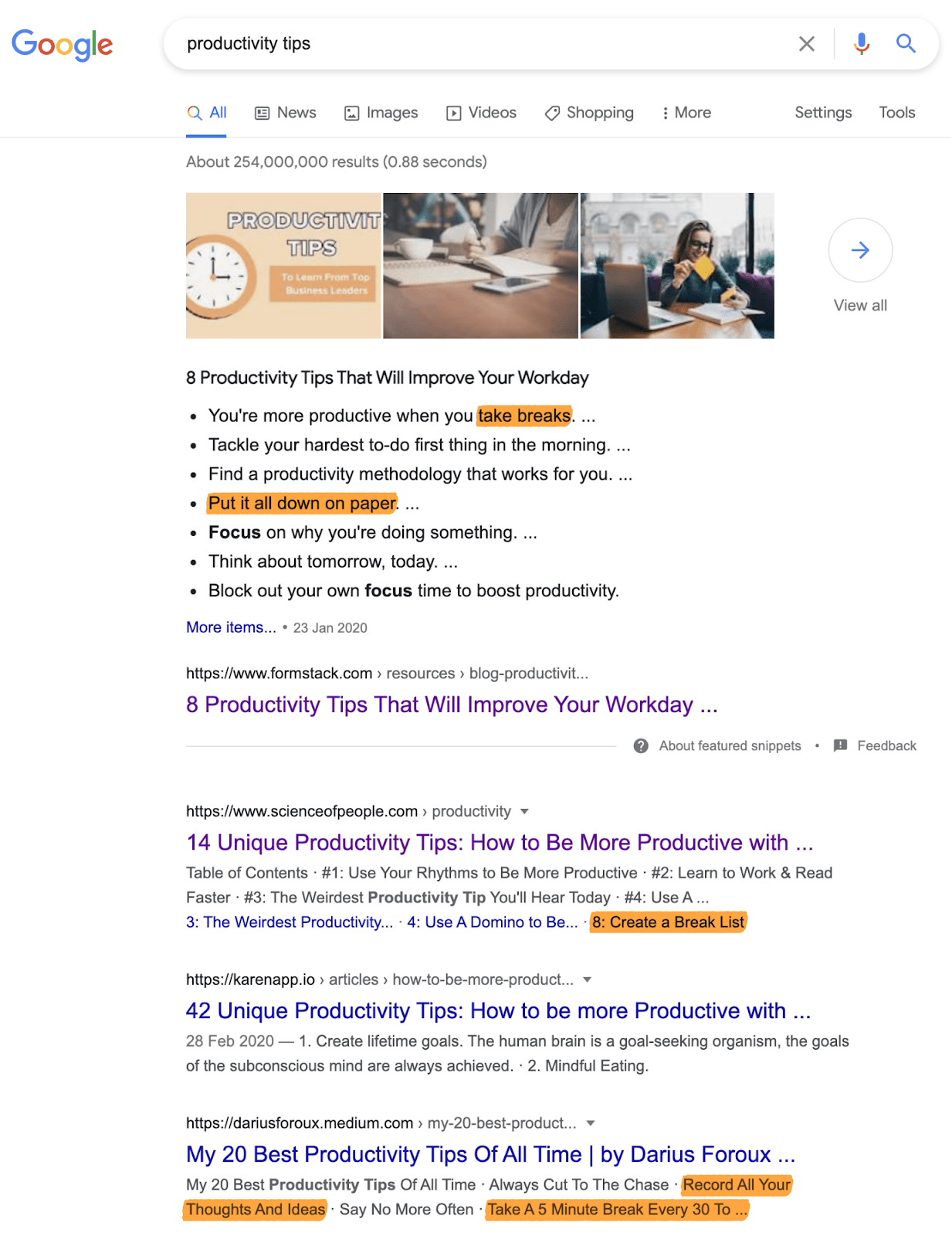
Although there’s nothing wrong with these tips, people searching for “productivity tips” probably want more practical ideas they can implement right away.
So you’d probably want to go beyond simple advice like “take breaks.”
23. Write a winning intro
If you can’t convince readers that your page offers what they want within a few seconds, they’ll hit that back button faster than you can say “dwell time.”
Your best defense against this is a compelling intro.
Good introductions should do three things:
- Connect with the reader
- Build trust
- Promise a solution to the user’s problem
Remember, if visitors never get past your introduction, they never read your content. And if they never read your content, they won’t convert, share, or link to it.
Learn one way to write a winning intro here.
24. Use headings to create hierarchy
Headings like H1 and H2 help to create hierarchy and break your content into logical sections. This makes your content easier to skim and digest.
For example, the list that you’re reading right now is broken into five distinct sections.
- SEO basics checklist
- Technical SEO checklist
- Content checklist
- On-page SEO checklist
- Link building checklist
Under each of these, we have sub-sub headings for each checklist item.
Think about how much harder it would be to read this page without subheadings.
Recommended reading: What is an H1 Tag? SEO Best Practices for 2021
25. Break things up with images
Nobody wants to read a big wall of text. It’s overwhelming and can lead people to bounce.
Images help solve this by breaking up your copy and aiding visual comprehension.
But don’t just throw images in for the sake of it. Make an effort to find or create images that improve the reader’s experience.
For example, we often use graphs, charts, and screenshots to help illustrate our points.
26. Use short sentences and paragraphs
50% of the US population read below an 8th-grade reading level.
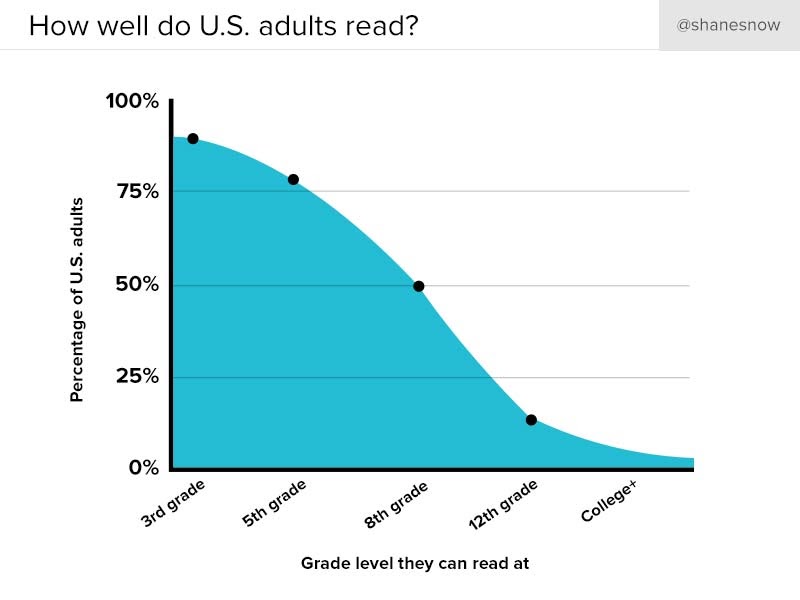
So unless you want to alienate half of the population, don’t overcomplicate things. Stick to short sentences and paragraphs.
You should also:
- Use simple words and phrases
- Avoid jargon
- Write in an active voice
Hemingway is a free, browser-based tool that can help with this. It tells you the current grade level of your copy and suggests improvements.

27. Add a table of contents
A table of contents provides jump links to different sections on the page.
We use them in most of our posts:

Although you can add a table of contents to any page, they’re best-suited to lengthy content that might otherwise be difficult to navigate. As most of our posts are 2,000+ words, they make a lot of sense for our visitors.
A table of contents can also help you win sitelinks in the SERPs.
Recommended reading: What Are Sitelinks? How to Influence Them
On-page SEO is the process of optimizing the actual content on your page. It includes optimizations made to visible content and content in the source code.
Let’s look at how to do it.
28. Use a short, descriptive URL
Short, descriptive URLs help searchers to understand what the page is about in the SERPs.
For example, these two pages are about losing weight…
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322345
https://www.dietdoctor.com/how-to-lose-weight
… but you wouldn’t know it from that first URL.
Most of the time, the simplest way to create short, descriptive URLs is to set your primary keyword as the URL slug. We do this with most of our blog posts.
ahrefs.com/blog/on-page-seo/
ahrefs.com/blog/link-building/
ahrefs.com/blog/free-seo-tools/
Keeping URLs short is useful because long URLs tend to truncate in the SERPs.
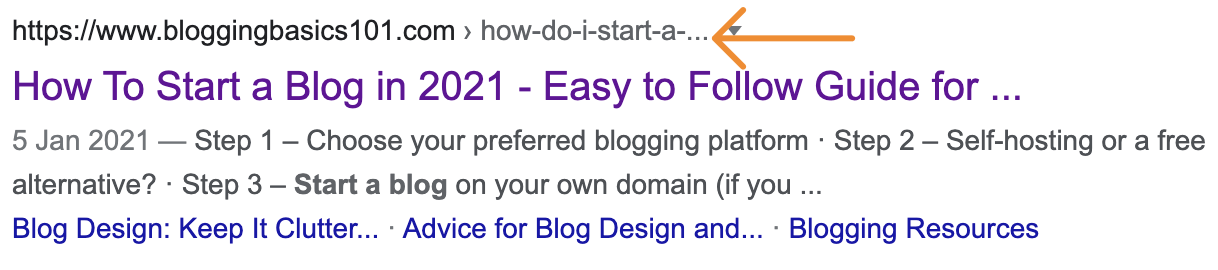
Recommended reading: How to Create SEO-Friendly URLs (Step-by-Step)
29. Write a compelling title tag
Like URLs, title tags show up in Google’s search results and help searchers understand what the page is about.
Common advice for title tags is to include your target keyword.
Although that’s good practice, don’t sweat it if it doesn’t make sense. It’s much more important to write something compelling that will make people want to click.
Most of the time, your post or page title will work well.
Recommended reading: How to Craft the Perfect SEO Title Tag
30. Write a compelling meta description
Google shows meta descriptions in the SERPs roughly ⅓ of the time.
Here are our best tips for creating a compelling meta description:
- Expand on the title
- Double down on search intent
- Use an active voice
- Keep it under 120 characters
- Include your primary keyword (where it makes sense)
Recommended reading: How to Write the Perfect Meta Description
31. Link to relevant resources
Linking to other internal resources helps visitors to navigate your website.
But what about external resources?
Here’s what Google’s John Mueller says:
Linking to other websites is a great way to provide value to your users. Oftentimes, links help users to find out more, to check out your sources and to better understand how your content is relevant to the questions that they have.
Does this mean you have to force internal and external links into your content?
Nope. Just add links if and when it makes sense.
Recommended reading: Internal Links for SEO: An Actionable Guide
32. Optimize your images
If you’re following the checklist in order, you should have already installed an image compression plugin. But there are a couple of other image optimizations you should do on a page by page basis:
- Name images descriptively. Don’t use generic image filenames like IMG_875939.png or Screenshot-2021–06-01. Use descriptive filenames like black-puppy.png or eiffel-tower.jpg.
- Add descriptive alt text. Alt text replaces an image on the page when it fails to load. It’s also helpful for those using screen readers. Learn more here.
Recommended reading: Image SEO: 12 Actionable Tips for More Organic Traffic
33. Add schema markup for rich snippets
Schema markup helps search engines to understand your content better. But it can also dramatically affect how your page shows up in the SERPs.
Here’s a page with schema markup that currently ranks for “pizza dough recipe:”

Here’s what it would look without schema markup:

Do you see the difference?
Schema markup can increase click-through rates and bring more traffic to your website.
It’s not that technical to implement either. Use Google’s markup helper or this Schema markup generator to do it with ease.
Recommended reading: Rich Snippets: What Are They and How Do You Get Them?
34. Add internal links
Internal links help Google understand what your page is about. They also help search engines and users to navigate your website.
We already covered the importance of linking to relevant internal and external resources in your content. But it’s also worth adding internal links from other relevant pages whenever you publish new content.
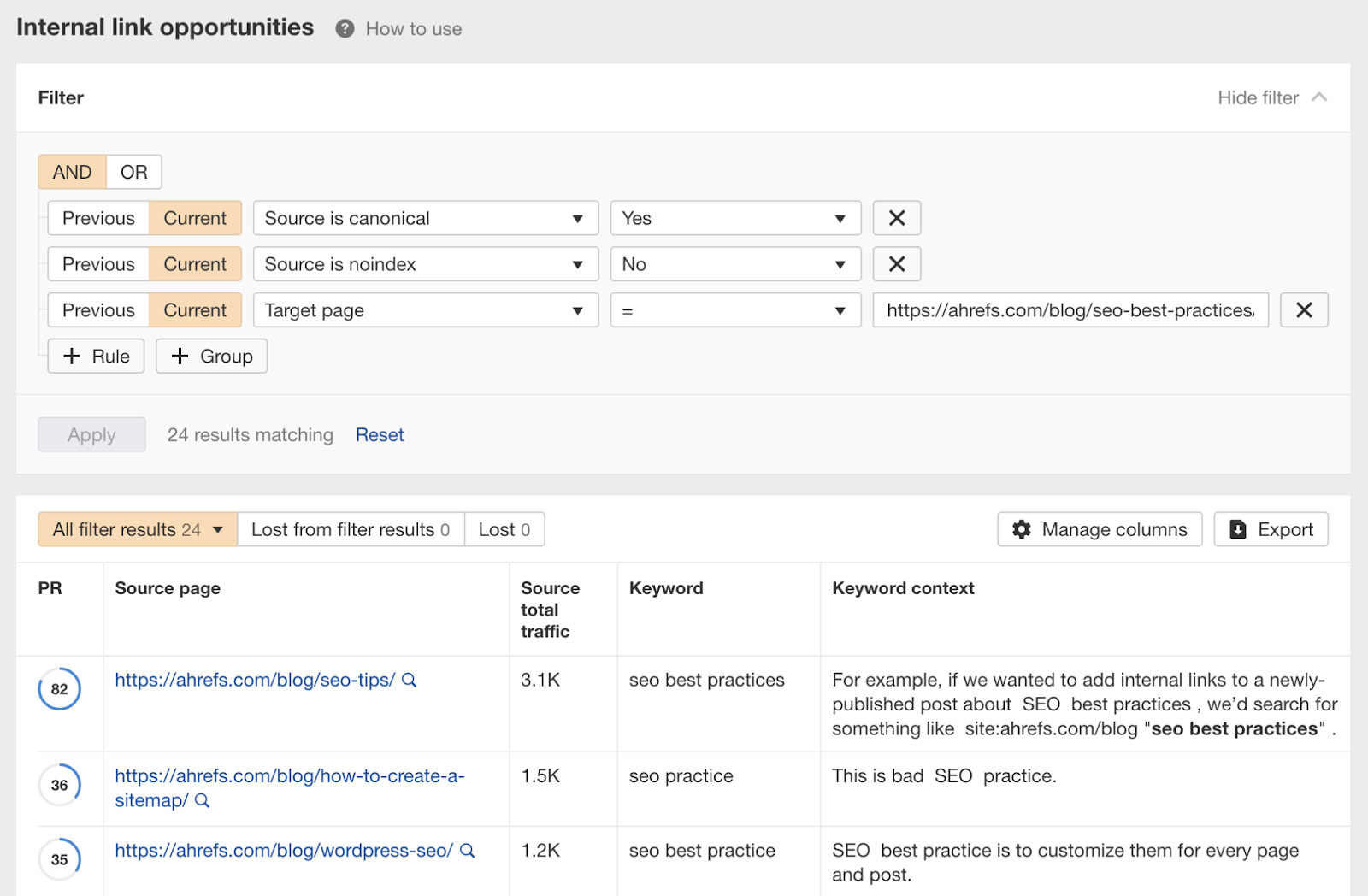
Here’s how to find relevant internal link opportunities:
- Create a free Ahrefs Webmaster Tools account
- Crawl your website with Site Audit
- Go to the Link Opportunities report
- Add a “Target page” filter and set it to your new page
Add internal links to those pages wherever it makes sense.
Link building is a crucial SEO task, especially if you want to rank for anything remotely competitive. In this section, we’ll cover a few tried and tested link building tactics.
Sidenote.
Some of these tactics are focused on building backlinks to your website as a whole, whereas others are focused on building backlinks to individual pages.
35. Replicate your competitors’ links
If a page is mentioning and linking to multiple competitors, but not you, it might be a link worth pursuing.
Here’s how to find these websites:
- Go to Content Explorer
- Search for (“competitor 1” AND “competitor 2”) -“your brand”
- Hit search
- Toggle “One page per domain”
This will search our database of over seven billion pages for those mentioning both your competitors, but not you.
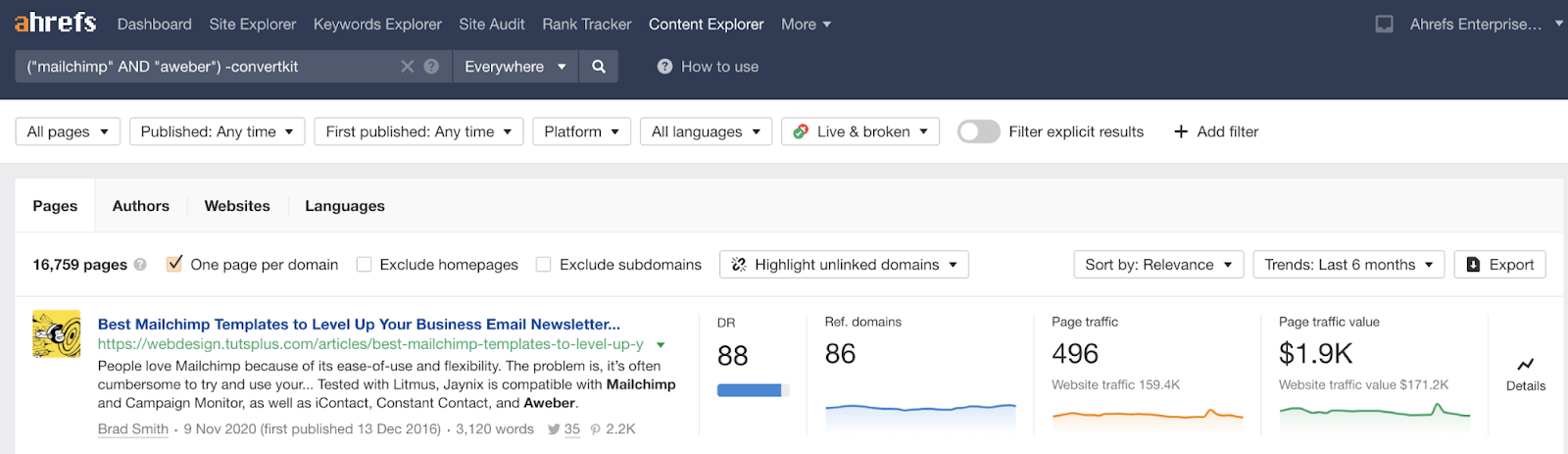
Then it’s just a case of looking for opportunities where you might be able to get a link.
For example, if you were doing this for ConvertKit, this list of 79 marketing tools would probably be a good opportunity:

36. Reclaim lost links
Backlinks don’t last forever.
For example, if we check the Lost Links report in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer for the Ahrefs Blog, we see hundreds of lost links in the last 7 days.
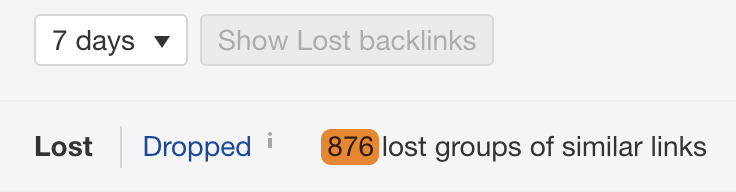
This happens for all kinds of reasons. Sometimes they’re gone for good. Other times it’s possible to reclaim them.
Recommended reading: Link Reclamation: How to Easily Find (and Reclaim) Lost Backlinks
37. Pursue unlinked mentions
People will sometimes mention your brand without linking to you. These are known as unlinked mentions.
Here’s an example of one:

You can see that even though they mention Ahrefs, they don’t link back to us.
Now, wouldn’t it be cool if you could convert unlinked mentions for your brand to linked mentions?
It would, and you can. Just reach out to the authors and request that they “make the text clickable.” Because they’re already familiar with your brand, there’s a high chance that they’ll happily make that change for you.
However, the question remains: How do you find unlinked brand mentions in the first place?
Everything is explained in the guide below.
Recommended reading: A Simple Guide to Turning (Unlinked) Brand Mentions into Links
38. Publish guest posts
Guest blogging is where you write and publish an article on another site in your industry.
For example, here’s a guest post by Ryan Stewart on the Ahrefs Blog:

Most people let guest authors link to their website from their author bio.
There are many ways to find guest blogging opportunities, but a simple method is to search for sites that have already written about relevant topics. Why? Because those sites are likely to be interested in a guest post about a similar topic.
Here’s how to find these sites:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Content Explorer
- Enter a relevant topic (e.g., “keyword research”)
- Choose “In title” from the drop-down
- Hit “Search”
- Go to the “Websites” tab
Here you should see the top 100 websites with the most organic traffic from pages about your topic.
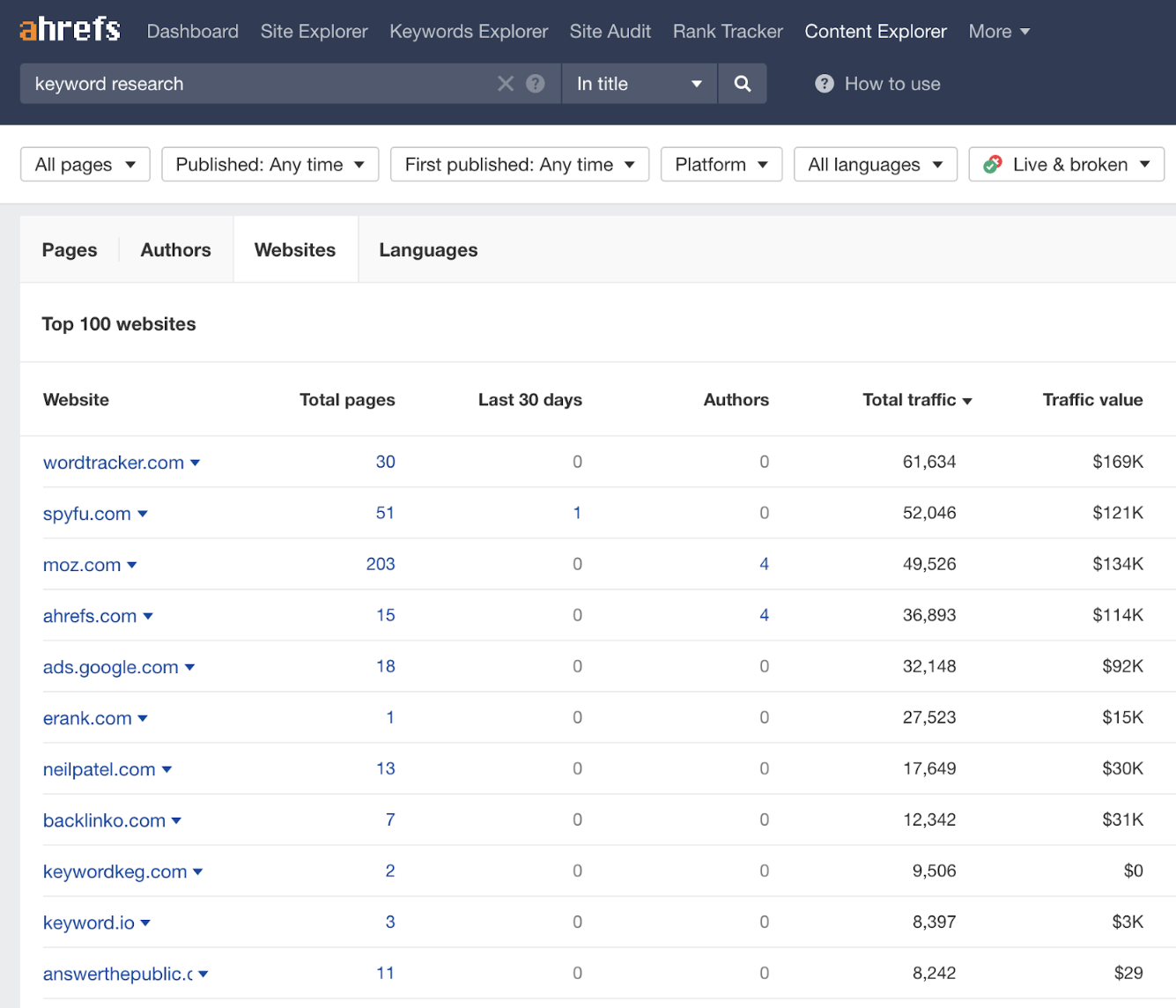
Look through the list and reach out to any relevant sites.
Recommended reading: Guest Blogging for SEO: How to Build High-quality Links at Scale
39. Pitch resource pages
Resource pages are pages that curate and link to resources about a topic.
You can find relevant resource pages using Google search operators like:
- [topic] intitle:resources inurl:resources.html
- [topic] intitle:links inurl: resources.html
- [topic] inurl:.com/resources
- [topic] inurl:resources intitle:resources
For example, here’s a resource page listing digital marketing resources:

It would make sense to pitch an SEO resource for that list.
40. Find people linking to inferior content
If you’ve put some effort into creating the best piece of content about a topic, there should be countless posts that aren’t as good as yours.
People linking to these posts are perfect link prospects.
For example, here’s a post about long-tail keywords with an inaccurate definition (it has nothing to do with length):

If we plug the post’s URL into Site Explorer, we see it has links from over 1,000 websites.

So we could easily reach out to those people, explain the issue, and suggest they link to our post about long-tail keywords with an accurate definition instead.
How do you find similar posts with lots of backlinks?
Follow these steps:
- Go to Content Explorer
- Search for your topic (e.g., long tail keywords)
- Choose “In title” from the drop down
- Filter for pages with lots of referring domains (linking websites)
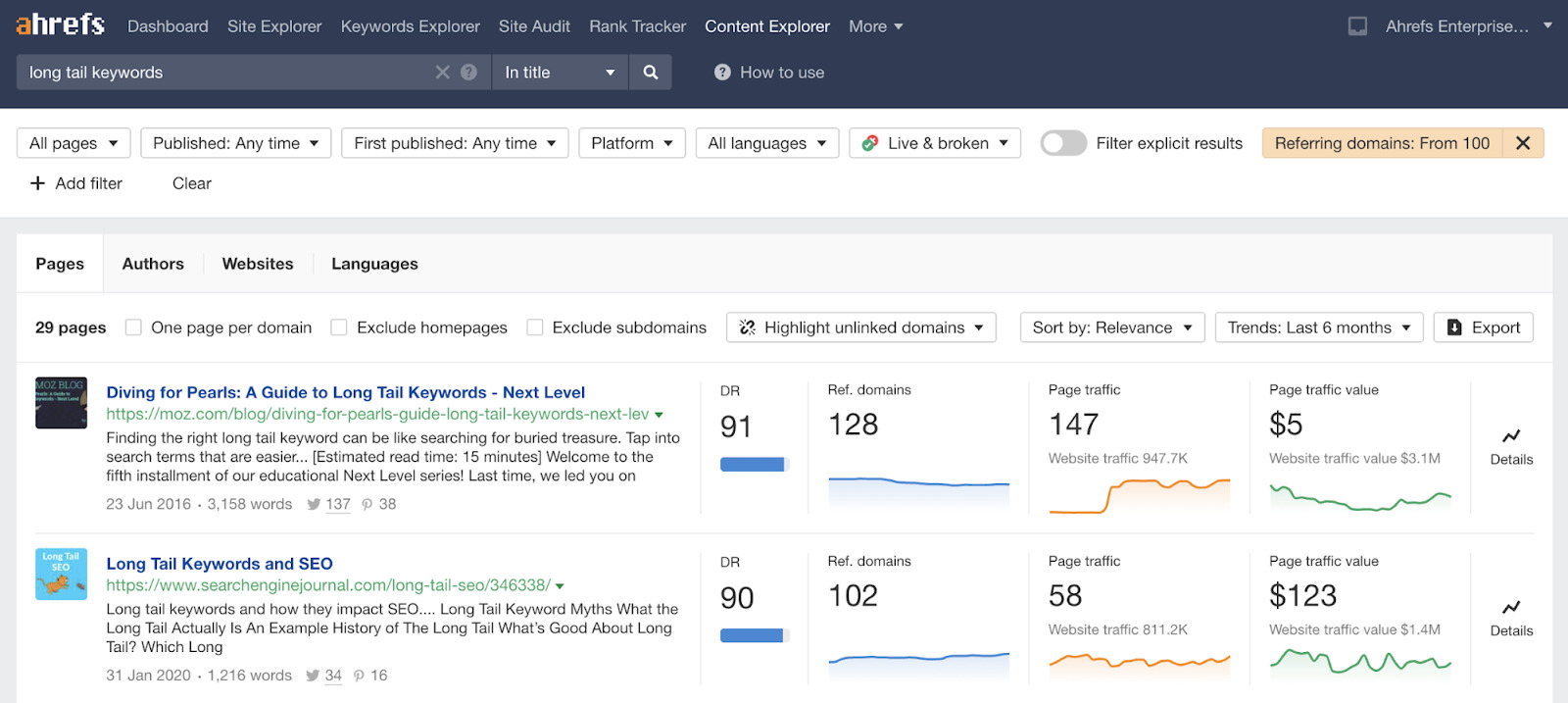
Then it’s just a case of finding a compelling reason why someone should link to your page over theirs.
41. Tell more people about your content
People can’t link to content if they don’t know it exists. That’s why you should make a conscious effort to tell the right people about your content.
But who are the “right” people?
They have two attributes:
- They are interested in your content
- They have the power to link to you
Learn how to find the right people to contact here, and how to reach out to them using this outreach advice.
Final thoughts
SEO is an ongoing process, and it would be impossible to include everything that’s important in one checklist. Having said that, if you tackle the checklist items above, you’ll be well on your way to higher rankings. You’ll also probably be well ahead of your competition. That’s all that matters.
If you’re looking to learn more about executing on this checklist, check out our free SEO training course.
Want even more SEO ideas? Check out our list of SEO tips.


